-
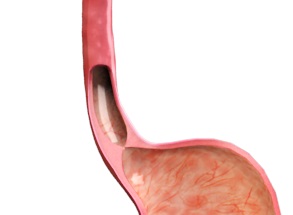
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)

Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a condition where the stomach acid leaks into your food pipe (oesophagus) causing a burning sensation in your chest and other associated symptoms.
Know More Launch Movie -
Irritable Bowel Syndrome

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a set of gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, discomfort, cramping, and bloating occurring together due to the abnormal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (usually the large intestine).
Know More -
Inflammatory Bowel Disease

The term inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refers to a group of intestinal disorders that cause chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract or digestive tract. Prolonged inflammation can result in the destruction or damage of the walls of the intestines, leading to the formation of sores and narrowing of the intestines.
Know More -
Crohn's Disease

Crohn’s disease is chronic inflammation of the bowel or digestive tract. Inflammation may occur in any region of the digestive system and is different for every patient. The inflammation of the bowel tissue spreads to deeper layers causing serious complications.
Know More -
Indigestion

Indigestion also known as dyspepsia refers to gastrointestinal symptoms characterized by pain and discomfort in the upper part of the abdomen.
Know More -
Diarrhoea

Diarrhoea is loose, watery, frequent bowel movements resulting in the elimination of water and salts from the body and can result in dehydration. Diarrhoea can be acute or chronic.
Know More -
Bowel Incontinence

It is an inability of a person to control bowel movements resulting in leakage from the rectum. It is also called faecal incontinence. The chances of older individuals developing bowel incontinence are higher than young individuals.
Know More -
Unintentional Weight Loss

Weight loss normally occurs due to the burning of calories from energy expenditure or a decreased calorie intake. Unintentional weight loss is loss of weight that comes without exercise or a change in diet or routine. It can be a symptom of an illness or serious medical condition and needs to be evaluated by a medical professional.
Know More -
Constipation

Constipation is a condition where stools or bowel movements become hard and difficult to expel from the body. This can result in fewer and strained bowel movements. It usually occurs when excessive water is absorbed from the stool while inside the colon. Constipation is a common condition that affects almost everyone at some time.
Know More -
Upper Gastrointestinal Disease

The gastrointestinal tract (GI) extends from the mouth to the anus. It is divided into upper and lower GI tracts. The upper gastrointestinal tract encompasses the mouth, oesophagus, stomach and duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
Know More -
Swallowing Disorders

Swallowing disorder, also known as dysphagia, is a difficulty in swallowing food or liquids. Swallowing is a set of coordinated muscle movements that control the mouth, the back of the throat (pharynx), and the food tube (oesophagus).
Know More -
Oesophageal Motility Disorder

Oesophageal motility refers to the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the oesophagus or food pipe to produce a wave-like motion that propels food and liquids from the mouth towards the stomach.
Know More -
Achalasia

Achalasia, also known as oesophageal achalasia, is a condition in which the oesophagus (a tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach) is unable to move the food into the stomach. A lower oesophageal sphincter is a ring of muscle fibres that surrounds the lower-most end of the oesophagus where it joins the stomach.
Know More -
Gastric Disease

Gastric disease refers to any disease that disrupts the normal functioning of the stomach.
Know More -
Gastritis

Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It is of two types: acute gastritis (sudden, short-lived inflammation) and chronic (long-term inflammation of gradual onset that may last years if not treated).
Know More Launch Movie -
Gastric Ulcers

Gastric ulcers also known as stomach ulcers are the formation of open sores in the lining of the stomach.
Know More -
Peptic Ulcer

A peptic ulcer is an open sore that develops on the inner lining of the stomach, the upper portion of the small intestine, or the oesophagus.
Know More -
Gastroparesis

Gastroparesis, also known as delayed gastric emptying, is a condition in which the stomach takes longer than usual to empty food into the intestine resulting in early satiety, nausea, and other symptoms.
Know More -
Gallbladder Disease

Gallbladder disease is an umbrella term for several conditions affecting the gallbladder. Inflammation of the gallbladder wall (cholecystitis) is responsible for a majority of the gallbladder diseases. Diseases of the gallbladder include gallstones, gallbladder polyps, gallbladder cancer, and sclerosing cholangitis.
Know More -
Gallstones

Gallstones is an umbrella term for several conditions affecting the gallbladder. Inflammation of the gallbladder wall (cholecystitis) is responsible for a majority of the gallbladder diseases. Diseases of the gallbladder include gallstones, gallbladder polyps, gallbladder cancer, and sclerosing cholangitis.
Know More Launch Movie -
Liver Disease

Liver disease is any disorder of the liver that impairs its normal function and can range from minor infection or scarring to serious conditions such as liver cancer. More than 100 types of liver disease have been identified.
Know More -
Fatty Liver Disease

Fatty liver disease is a condition caused by excess fat buildup in the liver cells. It is most common in middle-aged people. Fatty liver disease is also called hepatic steatosis.
Know More -
Hepatitis

Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver tissue. The liver is situated in the upper right portion of your abdomen and performs some of the body’s vital functions...
Know More -
Hepatitis A

Hepatitis A is a type of infectious viral disease characterised by inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus that is typically transmitted through eating or drink something contaminated with faecal matter.
Know More -
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is a viral infection affecting the liver that is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). There are two forms of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic. Acute hepatitis B usually lasts up to 6 months and is mainly seen in adults.
Know More -
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus that is typically transmitted through contaminated blood and can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, leading to severe liver damage.
Know More -
Liver Masses

Liver masses or lesions are a group of abnormal cells in your liver. They appear as a solid mass or nodules that can be differentiated from the normal liver tissue. The liver is one of the largest organs of the human body and is situated in the upper right portion of your abdomen.
Know More -
Hepatobiliary Disease

Hepatobiliary disease is any disorder of the hepatobiliary system that impairs its normal function. The disease can range from minor infection or scarring to serious conditions such as cancer. The organs of the hepatobiliary system are the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.
Know More -
Pancreatobiliary Diseases

Pancreatobiliary diseases are disorders or abnormalities of the pancreas, bile ducts, or gallbladder. The different types of disorders that may occur in these structures include obstruction, leakage, tumours, and lesions resulting in a variety of gastrointestinal problems.
Know More -
Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Malignancy or Pre-Malignant Conditions

Gastrointestinal malignancies are cancerous tumours or lesions that may arise anywhere in the gastrointestinal system which includes the stomach, oesophagus, gallbladder, liver, bile duct, colon, rectum, and anus. Pre-malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal system are characterized by abnormal lesions or cells that have a high risk of developing into gastrointestinal cancer.
Know More -
Liver Cancer

Cancer is the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells. Liver cancer may begin as a mass of abnormal cells called a tumour. Benign tumours remain localised and do not spread to neighbouring tissues. Malignant tumours begin to spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes or organs, disrupting their function.
Know More -
Pancreatic Cancer

The pancreas is a dual functioning gland of the digestive system made up of two types of cells: one produces digestive juices and the other releases hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels. The abnormal growth of pancreatic cells can lead to pancreatic cancer.
Know More -
Biliary Tract Cancer

Bile is a dark-green to the yellowish-brown fluid secreted by the liver. The gallbladder is a small organ nestled below the liver that stores bile. The bile duct carries bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine to facilitate fat-digestion.
Know More -
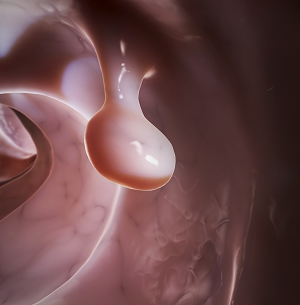
Polyp to Colon Cancer Progression

Colon cancer usually starts in an area of excess tissue growth in the inner lining of the colon or rectum called a polyp. Colon polyps occur in about 25% of the population over the age of 50. A small percentage of polyps may eventually progress to cancer and this usually takes several years.
Know More -
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)

Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition characterized by an abnormal increase of bacteria in the small intestine that may be associated with abdominal pain, malnutrition, or other symptoms. In most cases, these bacteria do not normally reside in the small intestine but arrive from other parts of the gut.
Know More -
Eosinophilia and Eosinophil-Associated Gastrointestinal Disorders (EGIDs)

Eosinophilia is a chronic disorder ensuing from the extreme production of eosinophils, either in the blood or in body tissues. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that resists infections and plays a role in the body's immune response. Generally, the blood doesn't have a large number of eosinophils.
Know More -
Inflamed or Irritable Bowel

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are two gastrointestinal disorders that are often confused for one other because of a few common symptoms. If you experience changes in your bowel movements, such as diarrhoea or constipation, cramping, and recurrent abdominal discomfort or pain, you may be suffering from either inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome.
Know More -
Coeliac Disease

Coeliac disease is a condition characterized by inflammation of the lining of the small intestine due to an autoimmune reaction (body’s immune system mistakenly attacks own healthy tissues) against gluten, a protein found in foods such as oats, wheat, rye, and barley. Intake of such foods may lead to gastrointestinal and malabsorptive problems.
Know More -
Diverticular Disease

The intestine is divided into the large and small intestines. The large intestine absorbs nutrients from the food that you eat and pushes the remaining undigested waste towards the anus. High fibrous foods like fruits and vegetables soften the undigested material and help in easy movement of stools. However, low-fibre foods can produce small and hard stools that are expelled with increased strain while passing.
Know More -
Diverticulosis

Diverticulosis is a condition characterized by the formation of diverticula, which are tiny pouch-like structures along the lining of the digestive tract. Diverticula are commonly found in the lower portion of the large intestine.
Know More -
Diverticulitis

Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation or infection of one or more diverticulum. Diverticula are tiny pouch-like structures that may be found in the intestinal wall, especially in older individuals.
Know More -
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding

Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) refers to haemorrhage or bleeding that occurs in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract (the oesophagus, the stomach, or the upper segment of the small intestine) as a result of inflammation or injury.
Know More -
Rectal Bleeding

Rectal bleeding refers to the passage of blood through the anus along with the stools. The rectum is the last part of the large intestine present just above the anus. Rectal bleeding is referred to as bright red to dark maroon coloured blood passing along with stools through the anus. The amount of blood loss varies from mild traces to severe life-threatening bleeds.
Know More -
Prevention of Gastrointestinal Diseases

Gastrointestinal (GI) diseases occur due to structural and functional abnormalities of the stomach and intestine. They can range from common digestive problems such as diarrhoea, nausea and abdominal cramps to chronic disorders including Crohn’s disease, coeliac disease, acid reflux, gallstones, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), colitis or cancer.
Know More